[JPA] CASCADE(영속성 전이)와 고아객체
자바 ORM 표준 JPA 프로그래밍 - 기본편 - 인프런 | 강의
이 글은 인프런에서 제공하는 자바 ORM 표준 JPA 프로그래밍 - 기본편 강의를 참고했고
강의 내용을 다시 복습하면서 정리하려는 목적으로 작성합니다.
자바 ORM 표준 JPA 프로그래밍 - 기본편 - 인프런 | 강의
JPA를 처음 접하거나, 실무에서 JPA를 사용하지만 기본 이론이 부족하신 분들이 JPA의 기본 이론을 탄탄하게 학습해서 초보자도 실무에서 자신있게 JPA를 사용할 수 있습니다., - 강의 소개 | 인프런
www.inflearn.com
이번에 포스팅하는 내용은 연관관계 매핑과 전혀 관련 없는 내용입니다.^^

CASCADE
특정 엔티티를 영속 상태로 만들고, 연관된 엔티티도 함께 상속상태로 만들고 싶을때 CASCADE를 사용합니다.
하나의 특정 엔티티(부모)가 연관된 엔티티(자식)를 관리할 때 사용하면 유용합니다.
갑자기 뜬금 없이 무슨말이냐구요?
게시글(부모)과 파일(자식)로 예를 들수 있겠습니다.
만약 게시글의 첨부파일을 해당 게시글만 관리하면?
cascade 기능을 사용하면 좋습니다.
쉽게 말해서, 게시글(부모)이 첨부파일(자식)만 연관관계가 있을 때 사용하는게 좋습니다.
(소유자가 1명일 때 사용하는 것을 권장 합니다.)
하지만, 첨부파일을 다른곳에서도 관리한다면 사용하지 않는게 좋습니다.
(소유자가 여러명이면 사용하지 마세요.!)
CASCADE 종류
- ALL: 아래 기술된 모든 동작을 연관된 엔티티에게 전파
- PERSIST:
persist가 특정 엔티티에서 연관된 엔티티에게 전파 - REMOVE: 특정 엔티티 삭제시 연관된 엔티티도 동시에 삭제
- MERGE: 특정 엔티티가 업데이트 될때 연관된 엔티티도 업데이트
- REFRESH: 데이터베이스로부터 데이터를 다시 읽어오는
refresh동작을 특정 엔티티에서 연관된 엔티티로 전파 - DETACH:
detach를 특정 엔티티에서 연관된 엔티티로 전파
먼저 CASCADE를 사용하지 않았을때를 보여 드리겠습니다.

Post(부모)
@Entity
@Getter @Setter
public class Post {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private String name;
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "post")
private List<File> files = new ArrayList<>();
public void changePost(File file) {
files.add(file);
file.setPost(this);
}
}
File(자식)
@Entity
@Getter @Setter
public class File {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private String name;
private String path;
// 연관관계 주인
@ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY)
@JoinColumn(name = "file_id")
private Post post;
}
실험
tx.begin();
File file1 = new File();
file1.setName("둘리");
file1.setPath("/image/둘리.png");
File file2 = new File();
file2.setName("도우너");
file2.setPath("/image/도우너.png");
Post post = new Post();
post.setName("아기공룡 둘리");
post.changePost(file1);
post.changePost(file2);
em.persist(post);
tx.commit();
결과
Hibernate:
/* insert com.study.purejpa.Post
*/ insert
into
Post
(name, id)
values
(?, ?)em.persist(usedCar)만 했기 때문에 insert SQL이 1개만 발생한 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
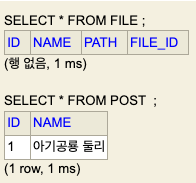
그렇다면 CASCADE PERSIST를 사용하면?
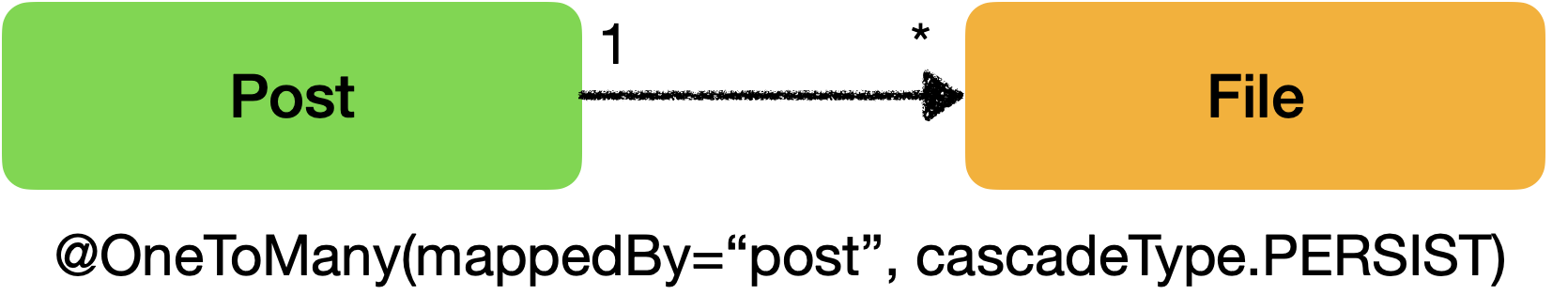
Post(부모)
@Entity
@Getter @Setter
public class Post {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private String name;
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "post", cascade = CascadeType.PERSIST)
private List<File> files = new ArrayList<>();
public void changePost(File file) {
files.add(file);
file.setPost(this);
}
}
결과
Hibernate:
/* insert com.study.purejpa.Post
*/ insert
into
Post
(name, id)
values
(?, ?)
Hibernate:
/* insert com.study.purejpa.File
*/ insert
into
File
(name, path, file_id, id)
values
(?, ?, ?, ?)
Hibernate:
/* insert com.study.purejpa.File
*/ insert
into
File
(name, path, file_id, id)
values
(?, ?, ?, ?)em.persist(usedCar)만 했는데도 insert SQL이 3개 발생한 것을 확인할 수 있습니다!!!
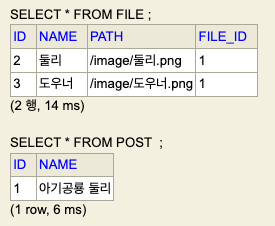
UsedCar를 영속화 하면 Dealer도 영속화가 됩니다.
쉽게 설명하면 영속화가 연쇄적으로 발생했다고 할수 있습다.

고아 객체
특정 엔티티(부모)와 연관관계가 끊어진 연관된 엔티티(자식)를 의미합니다.
고아 객체 판단 조건
고아 객체는 부모 엔티티와 연관관계가 끊어진 자식 엔티티를 의미 합니다.
- 부모 엔티티를 삭제하는 경우
em.remove(parent);
- 부모 엔티티에 있는 자식 엔티티(컬렉션)제거
em.parent.getChild().remove(0);
orphanRemoval = true
이러한 자식 엔티티를 자동으로 삭제하는 기능은 orphanRemoval = true 입니다.
참조가 제거된 엔티티는 다른 곳에서 참조하지 않는 고아 객체로 인식하고 삭제하는 기능입니다.
부모를 제거하면 자식은 고아가 됩니다.
따라서 고아 객체 제거 기능을 활성화 하면, 부모를 제거할 때 자식도 함께 제거 됩니다.
(마치 cascade = CascadeType.REMOVE 처럼 동작)
또한 부모 엔티티에 속해있는 자식 엔티티(컬렉션)을 제거하면 해당 엔티티를 고아 객체로 판단하여 제거 합니다.
반드시 참조하는 곳이 하나일 때 사용해야 합니다.
특정 엔티티가 자식 엔티티를 개인 소유할 때 사용해야 합니다.@OneToOne, @OneToMany 만 가능 합니다.
orphanRemoval = true를 설정 🙅♂️
File
@Entity
@Getter @Setter
public class File {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private String name;
private String path;
// 연관관계 주인
@ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY)
@JoinColumn(name = "file_id")
private Post post;
}
Post
@Entity
@Getter @Setter
public class Post {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private String name;
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "post")
private List<File> files = new ArrayList<>();
public void changePost(File file) {
files.add(file);
file.setPost(this);
}
}
실험
tx.begin();
File file1 = new File();
file1.setName("둘리");
file1.setPath("/image/둘리.png");
File file2 = new File();
file2.setName("도우너");
file2.setPath("/image/도우너.png");
Post post = new Post();
post.setName("아기공룡 둘리");
post.changePost(file1);
post.changePost(file2);
em.persist(post);
em.persist(file1);
em.persist(file2);
em.flush();
em.clear();
Post findPost = em.find(Post.class, post.getId());
// 부모와 연관관계 끊기
findPost.getFiles().remove(0);
tx.commit();
결과
Hibernate:
/* insert com.study.purejpa.Post
*/ insert
into
Post
(name, id)
values
(?, ?)
Hibernate:
/* insert com.study.purejpa.File
*/ insert
into
File
(name, path, file_id, id)
values
(?, ?, ?, ?)
Hibernate:
/* insert com.study.purejpa.File
*/ insert
into
File
(name, path, file_id, id)
values
(?, ?, ?, ?)
Hibernate:
select
post0_.id as id1_11_0_,
post0_.name as name2_11_0_
from
Post post0_
where
post0_.id=?
Hibernate:
select
files0_.file_id as file_id4_5_0_,
files0_.id as id1_5_0_,
files0_.id as id1_5_1_,
files0_.name as name2_5_1_,
files0_.path as path3_5_1_,
files0_.file_id as file_id4_5_1_
from
File files0_
where
files0_.file_id=?지연로딩으로 설정했기 때문에 findPost.getFiles().remove(0); 시점에서 select * from File ... SQL이 발생합니다.
그리고 orphanRemoval를 따로 설정하지 않아서 부모 엔티티와 자식 엔티티의 연관관계가 끊어졌음에도 delete SQL이 발생하지 않았습니다.
orphanRemoval = true를 설정 🙆♂️
orphanRemoval = true로 설정
@Entity
@Getter @Setter
public class Post {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private String name;
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "post", cacasde = CascadeType.ALL, orphanRemoval = true)
private List<File> files = new ArrayList<>();
public void changePost(File file) {
files.add(file);
file.setPost(this);
}
}cacasde = CascadeType.ALL 설정 이유
https://www.inflearn.com/questions/137740/orphanremoval%EA%B3%BC-cascade%EC%9D%98-%EA%B4%80%EA%B3%84
orphanRemoval과 cascade의 관계 - 인프런 | 질문 & 답변
안녕하세요 영한님 강의 정말 잘 듣고 있습니다! 다름이 아니라 orphanRemoval과 cascade의 명확한 차이를 공부하던 도중 이해가 가지 않는 것이 있어서 질문 드립니다! 환경은 Spring Boot 2.4.2 입니다. ca
www.inflearn.com
실험
tx.begin();
File file1 = new File();
file1.setName("둘리");
file1.setPath("/image/둘리.png");
File file2 = new File();
file2.setName("도우너");
file2.setPath("/image/도우너.png");
Post post = new Post();
post.setName("아기공룡 둘리");
post.changePost(file1);
post.changePost(file2);
em.persist(post);
em.persist(file1);
em.persist(file2);
em.flush();
em.clear();
Post findPost = em.find(Post.class, post.getId());
// 부모와 연관관계 끊기
// 자식 엔티티를 컬렉션에서 제거
findPost.getFiles().remove(0);
tx.commit();
결과
Hibernate:
/* insert com.study.purejpa.Post
*/ insert
into
Post
(name, id)
values
(?, ?)
Hibernate:
/* insert com.study.purejpa.File
*/ insert
into
File
(name, path, file_id, id)
values
(?, ?, ?, ?)
Hibernate:
/* insert com.study.purejpa.File
*/ insert
into
File
(name, path, file_id, id)
values
(?, ?, ?, ?)
Hibernate:
select
post0_.id as id1_11_0_,
post0_.name as name2_11_0_
from
Post post0_
where
post0_.id=?
Hibernate:
select
files0_.file_id as file_id4_5_0_,
files0_.id as id1_5_0_,
files0_.id as id1_5_1_,
files0_.name as name2_5_1_,
files0_.path as path3_5_1_,
files0_.file_id as file_id4_5_1_
from
File files0_
where
files0_.file_id=?
Hibernate:
/* delete com.study.purejpa.File */ delete
from
File
where
id=?부모 엔티티와 자식 엔티티의 연관관계가 끊어지니 자식 엔티티에 대한 delete SQL이 발생 했습니다.!!
만약 부모 엔티티(post)를 삭제하면?
실험
tx.begin();
File file1 = new File();
file1.setName("둘리");
file1.setPath("/image/둘리.png");
File file2 = new File();
file2.setName("도우너");
file2.setPath("/image/도우너.png");
Post post = new Post();
post.setName("아기공룡 둘리");
post.changePost(file1);
post.changePost(file2);
em.persist(post);
em.persist(file1);
em.persist(file2);
em.flush();
em.clear();
// 부모 엔티티 삭제
Post findPost = em.find(Post.class, post.getId());
em.remove(findPost);
tx.commit();
결과
Hibernate:
/* insert com.study.purejpa.Post
*/ insert
into
Post
(name, id)
values
(?, ?)
Hibernate:
/* insert com.study.purejpa.File
*/ insert
into
File
(name, path, file_id, id)
values
(?, ?, ?, ?)
Hibernate:
/* insert com.study.purejpa.File
*/ insert
into
File
(name, path, file_id, id)
values
(?, ?, ?, ?)
Hibernate:
select
post0_.id as id1_11_0_,
post0_.name as name2_11_0_
from
Post post0_
where
post0_.id=?
Hibernate:
select
files0_.file_id as file_id4_5_0_,
files0_.id as id1_5_0_,
files0_.id as id1_5_1_,
files0_.name as name2_5_1_,
files0_.path as path3_5_1_,
files0_.file_id as file_id4_5_1_
from
File files0_
where
files0_.file_id=?
Hibernate:
/* delete com.study.purejpa.File */ delete
from
File
where
id=?
Hibernate:
/* delete com.study.purejpa.File */ delete
from
File
where
id=?
Hibernate:
/* delete com.study.purejpa.Post */ delete
from
Post
where
id=?부모 엔티티를 삭제하면(em.remove(findPost);)
자식 엔티티가 먼저 삭제되고, 부모 엔티티가 삭제되는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
마치 CascadeType.REMOVE 처럼 동작 합니다.
정리
결과적으로 orphanRemoval = true를 설정하면
자식 엔티티(고아 객체)는 부모 엔티티와 함께 삭제 되거나, 자식 엔티티(고아 객체)만 삭제 됩니다.
CascadeType.ALL + orphanRemoval = true 2가지 옵션을 모두 활성화 하면 부모 엔티티를 통해서 자식의 생명 주기를 관리할 수 있습니다.
'0+ 스프링 > 0 + 스프링 ORM(JPA)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [JPA] JPQL 기본 개념과 예제 (0) | 2023.02.28 |
|---|---|
| [JPA] 잘 설계한 ORM 애플리케이션은 매핑한 테이블의 수보다 클래스의 수가 더 많다.(값 타입, 엔티티 타입) (1) | 2023.02.27 |
| [JPA] JPA가 Entity를 판별하는 방법과 save()의 비밀(entityInformation.isNew(entity)) (0) | 2023.02.22 |
| [JPA] 하이버네이트 프록시와 지연로딩(Lazy), 즉시로딩(Eager) (0) | 2023.02.22 |
| [JPA] @MappedSuperclass(공통 매핑 정보 해결 + 스프링 적용) (0) | 2023.02.20 |
